More businesses are going from offline to online. With over 5.7 million in e-commerce sales, it offers huge opportunities for businesses to make sales and profit. Although selling retail may have declined steeply in recent years, it remains relevant and an integral part of retail.
Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for any business looking to thrive in today’s market. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key differences between selling retail and e-commerce.

How E-commerce Works
E-commerce simply means buying and selling goods or services over the internet. It does not require physical structure or manual display of products. Here, sales are made in the online store or through any social channel.
Direct-to-customers and Dropshipping are the two methods of e-commerce sales that differ in their modes of operation.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping involves a third party, mostly wholesalers or manufacturers of the products who take care of order fulfilment and product shipment to the customer. In return, the retailer focuses on marketing and other areas of the business. New to Shopify, here are the 15 best dropshipping apps to try in your store.
Direct-to-Customer
The retailers own their inventory and sell and ship directly to customers. Third-party retailers or wholesalers are not involved here.
Steps to creating your e-commerce store
- First, create an online storefront, either a website or an app. This store features your product catalog that lists items and products available for purchase.
- From the catalog, customers can select products of their choice and add them to the shopping cart which is then processed at the checkout after payment.
- Once payment is confirmed, the business is responsible for order fulfillment, shipped to the customer through its courier services or a third-party logistic provider.
- Real-time tracking information is typically provided to the customer, allowing them to monitor the status of their order.
How Selling Retail Works
Retail selling is the conventional way of selling. It begins with the manufacturing of a product and ends with a consumer buying the product through retailers. It involves physical interactions between the buyer and sellers where customers can see and feel a product before making purchases.
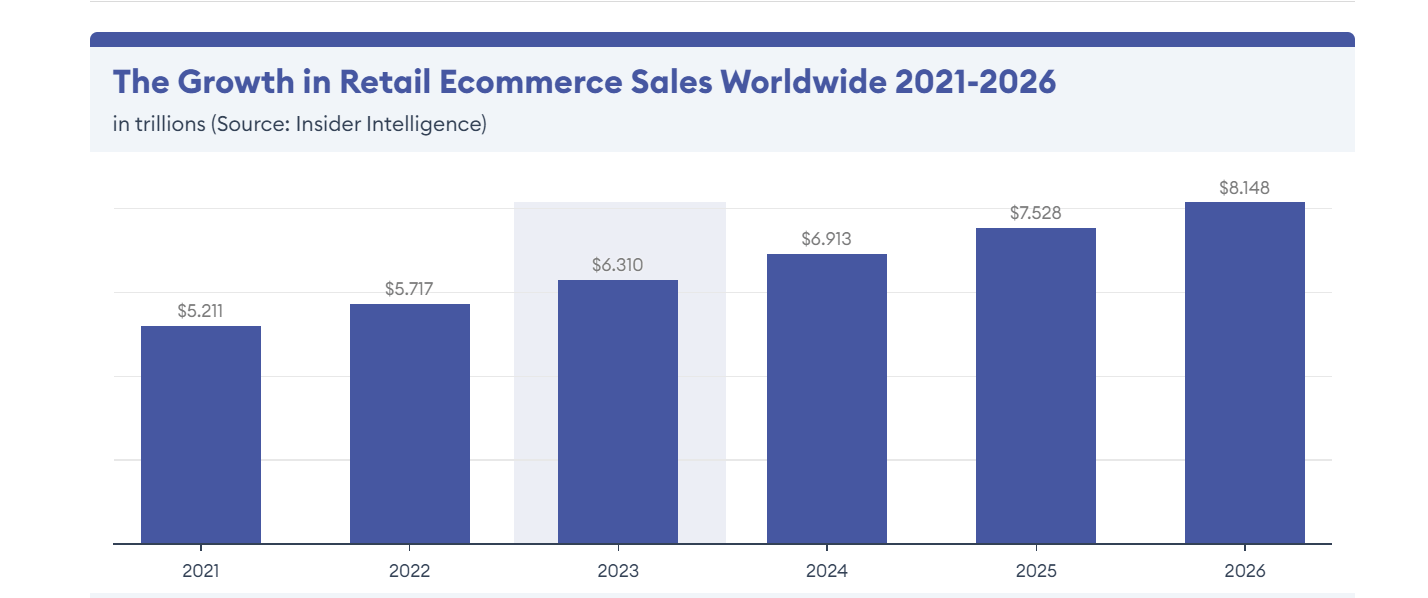
Popularly known as the brick-and-mortar store, physical retail is complex. However, it plays a significant role in the global economy. In 2021, global retail sales were around $26.4 trillion and are projected to increase to around $32.8 trillion by 2026.
How does selling in retail work?
- The process starts with retailers setting up their physical stores and designing an attractive and efficient layout to encourage customers to explore the store, find products easily and make the checkout process easier.
- Next is to decide what products to sell, supplier negotiation etc.
- Then, the inventory management which includes forecasting, ordering products and maintaining optimal stock levels. Setting the right prices for products while considering cost, competition and perceived product value.
- Lastly, marketing through their store or online platforms to reach potential customers and draw them into their stores.
Differences Between E-commerce and Retail
There are notable differences between e-commerce and retail in terms of product, pricing, personal shopping experience etc.
1. Capital
Setting up a physical retail store is capital and labour-intensive. It requires funds to cater for rent, lease, inventory purchase, marketing, insurance and other legal procedures.
While e-commerce requires little to no capital, all you need is to create an online presence. This includes buying and hosting your domain, creating your online store, and investing in marketing tools and inventory for your store. Inventories are not necessary if you are into dropshipping.
2. Products
In physical retailing, products are physically displayed where customers can see, touch and feel the product before the buying decisions. E.g. furniture, clothing, equipment etc. Even without a product description, you can match the size of each product with yours by merely looking at it.
In an online store, product images, descriptions and reviews influence buyers’ decisions. Bad ratings or blurry product images can affect purchases which affects revenue. However, shopping online gives you more room for price comparison from different e-commerce stores which helps to make better buying decisions.
For example, customers can feel the texture of clothing in stores before purchase, unlike online stores where you can only read the product description. Also, there are instances where smaller items are magnified on e-commerce stores and sold to customers as bigger items only for customers to be disappointed when the product is delivered. It is so bad that at least 30% of online products are returned compared to 8% in brick-and-mortar shops.
3. Cost of Operation
Overhead and Operational cost in brick-and-mortar shop is higher when compared to an online store. Retail stores require more manual work involving workers, the cost of maintaining employees, annual rents and legal and unavoidable costs.
While the cost is minimal in an e-commerce store since there is little or no labour, no physical location or inventories. Besides e-commerce processes are automated to increase efficiency and productivity from effective inventory management to AI tools for ecommerce.
4. Convenience
One advantage of online shopping is that you can do so anywhere from your phone, you don’t have to visit a store to shop. Browse a store and place an order immediately without having to stand in line or request help from a store rep. The only challenge is that you don’t instantly get what you order, it may take a while for your product to get shipped to you.
While in retail, you get your product once payment is verified. However, you can only do so while you are in the store and visiting the store can be stressful and time-consuming, however, the instant gratification of returning home with your product is worth it.
5. Customer Support Services
You don’t need customer support while shopping online and waiting on customer support to rectify problems can be frustrating when shopping online unlike the physical retail store where support is always available to assist you when needed and help in the checkout process.
Similarities in Selling Online vs Retail
1. Brand Identity
Whether you are an online or a brick-and-mortar shop, your brand identity matters. It gives your brand an identity and differentiates you from your competitors. Branding from scratch can be daunting, but building with the right strategies makes branding easy.
2. Product Arrangement and Layout
Cleaner layout and product arrangement make the shopping experience easier and faster for both retail and online stores. Valuable products are placed at eye level and in visible places where they are easily seen. For online stores, product recommendations are also one of the ways to introduce products to your customers.
3. Mode Of Operation
Although the cost and mode of operation may differ between the physical and online shops, it cannot be denied that it is essential for business success. Most businesses rely on it to track costs and manage inventory.
4. Risk
Risk is inevitable. Be it online or offline, every business opens itself up to some level of risk, whether it is the risk of liabilities ie the risk of being held accountable for action or inactions, whether or not at fault e.g use of products or injuries within the premises, and risk of theft.
4. Return Policy
30% of products ordered online are returned while 8.89% are returned in brick-and-mortar stores. In 2022, 10% of online returned orders were fraudulent which resulted in $22.8 billion lost in return fraud. Though online shoppers will choose companies with a return policy over one without, it is important to create an effective policy to keep returns at their lowest.
5. Product Delivery
Depending on the product size and proximity to the store, physical retailers offer product delivery to customers for a more personalized shopping experience and an increase in trust and loyalty. In addition, frequent retail customers may request for their preferred products to be delivered through a local courier or logistic company.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Retail vs E-commerce
Below are some of the factors to consider when choosing between retail and e-commerce.
1. Business Model
Some businesses thrive better as retail stores than online, especially when they require face-to-face interaction. Therefore, it’s important to ask the right questions before setting up your store.
2. Target Audience
- Demographics – Consider the age, location and preference of your target audience. Younger, tech-savvy consumers may prefer e-commerce, while older individuals might still prefer the in-person experience of retail.
- Accessibility – Think about how accessible your products are to your target audience. E-commerce can reach a broader audience, while retail might be more localized.
3. Cost Overheads
- Startup Costs – E-commerce typically has lower startup costs than traditional retail, as it requires physical store space, inventory and more staff members.
- Operating Costs – Consider ongoing expenses like rent, utilities and staff salaries. E-commerce may have a lower overhead, but it requires investments in technology and digital marketing.
4. Integration
Consider if you can benefit from integrating both retail and e-commerce. Some businesses operate hybrid models, offering the best of both worlds to cater to different customer preferences.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision between retail and e-commerce should be based on a comprehensible analysis of these factors and a clear understanding of your business’s unique strengths, weaknesses, and goals. It’s also worth considering hybrid models that combine both approaches to leverage the strengths of each while mitigating their respective weaknesses.
Looking to jumpstart your e-commerce journey with more sales? Add Adoric to your Shopify app tools to experience a 5x boost in conversion and sales.